Create A Quantum Bayesian Network
A practical guide
Bayesian networks are probabilistic models that model knowledge about an uncertain domain.
Bayesian networks build on the same intuitions as the Naïve Bayes classifier. But in contrast to Naïve Bayes, Bayesian networks are not restricted to represent solely independent features. They allow us to include as many interdependences that appear reasonable in the current setting.
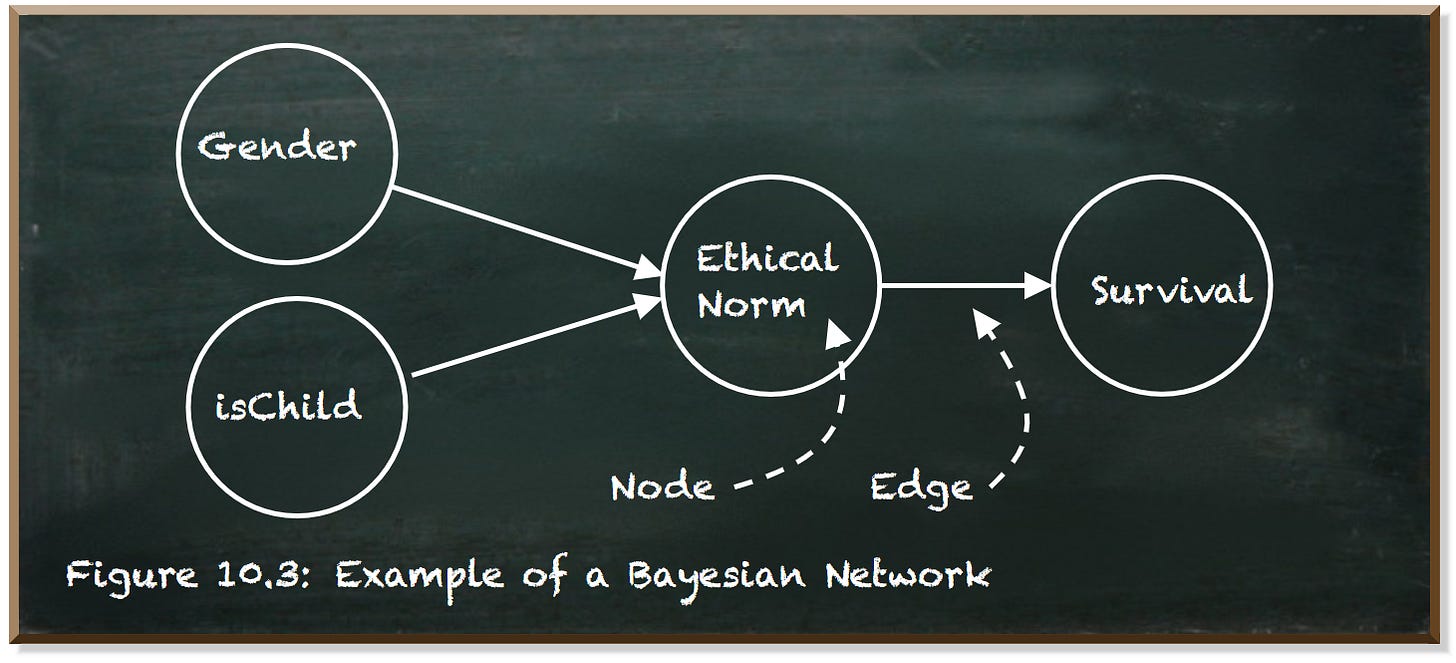
A Bayesian network is represented as a directed acyclic graph with nodes and edges.
The nodes represent random variables, such as the gender of a passenger or whether s/he was a child.
The edges correspond to the direct influence of one variable on another. In other words, the edges define the relationship between two variables. The directions of the arrows are important, too. The node connected to the tail of the arrow is the parent node. The node connected to the head is the child node. The child node depends on the parent node.
We quantify this dependence using conditional probability tables (CPT) for discrete variables and conditional probability distributions (CPD) for continuous variables.
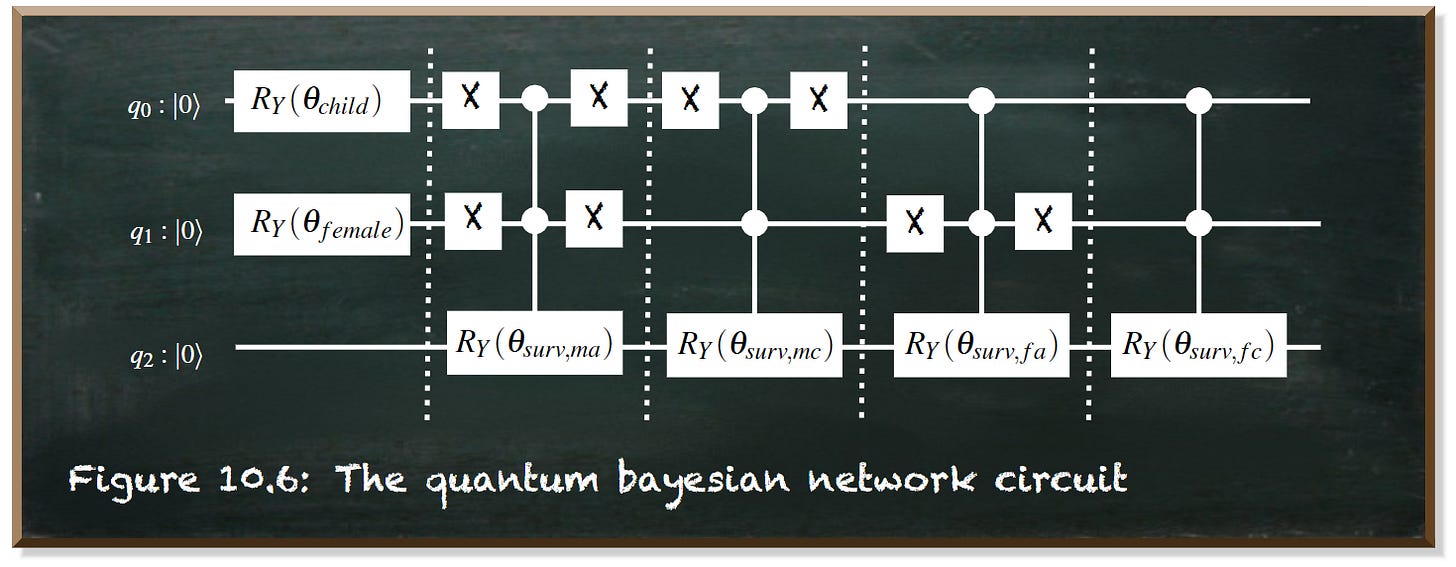
In today’s post, we create a Quantum Bayesian network with three nodes. We implement it in Qiskit and run our first inference.